In the realm of electrical safety standards, Class I, Class II, Class III, and Class 2 devices primarily revolve around considerations for the insulation systems. Let’s explore the definitions and differences among these classifications:
Class I, Class II, Class III Devices:
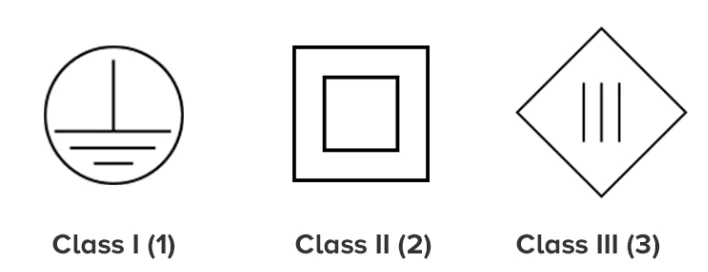
1. Class I Devices:
- Definition: These devices rely on essential insulation to prevent electric shock and provide additional protection through a protective ground impedance connected to the building. In the event of primary insulation failure, this ground impedance withstands hazardous voltages to the ground. Class I devices, such as switch-mode power supplies, offer a pair of terminals for ground connections.
2. Class II Devices:
- Definition: Class II devices depend on basic insulation for electric shock prevention and necessitate additional safety measures like double insulation or reinforced insulation. Importantly, they do not rely on a protective ground. In other words, Class II switch-mode power supplies do not provide a ground connection terminal.
3. Class III Devices:
- Definition: Devices falling under Class III derive their power from a Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) circuit, ensuring the absence of any hazardous voltage in the circuit.
Class 2 Devices:
The primary objective of Class 2 devices is to reduce the fire risk caused by the electronic circuit’s current and energy. When powered by Class 2, the circuit’s current and energy must adhere to the standards specified in UL1310 Table 30.1, significantly lowering the fire risk. This reduction allows for decreased spacing on the circuit and a lower fire rating for components, permitting the use of HB-grade plastic for the casing, ultimately contributing to cost savings. Class 2 devices are associated with UL class 2 Power units (UL1310).
Differences Between Class I and Class II:
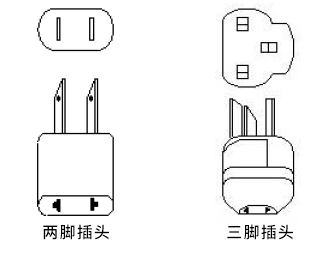
Appearance Description:
- Class I power supplies have a 3-pin AC input.
- Class II power supplies have a 2-pin AC input.
- Notably, the plug types differ between Class I and Class II devices.
Markings:
- Class I power supplies lack the “return” double insulation symbol.
- Class II power supplies feature the “return” double insulation symbol.
- Class II devices often include the ‘return’ type insulation symbol in their markings.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for engineers and manufacturers to ensure compliance with safety standards and make informed decisions when designing and evaluating electrical systems. Each class serves a specific purpose in mitigating electrical hazards and ensuring user safety.



